Definition and Symptoms
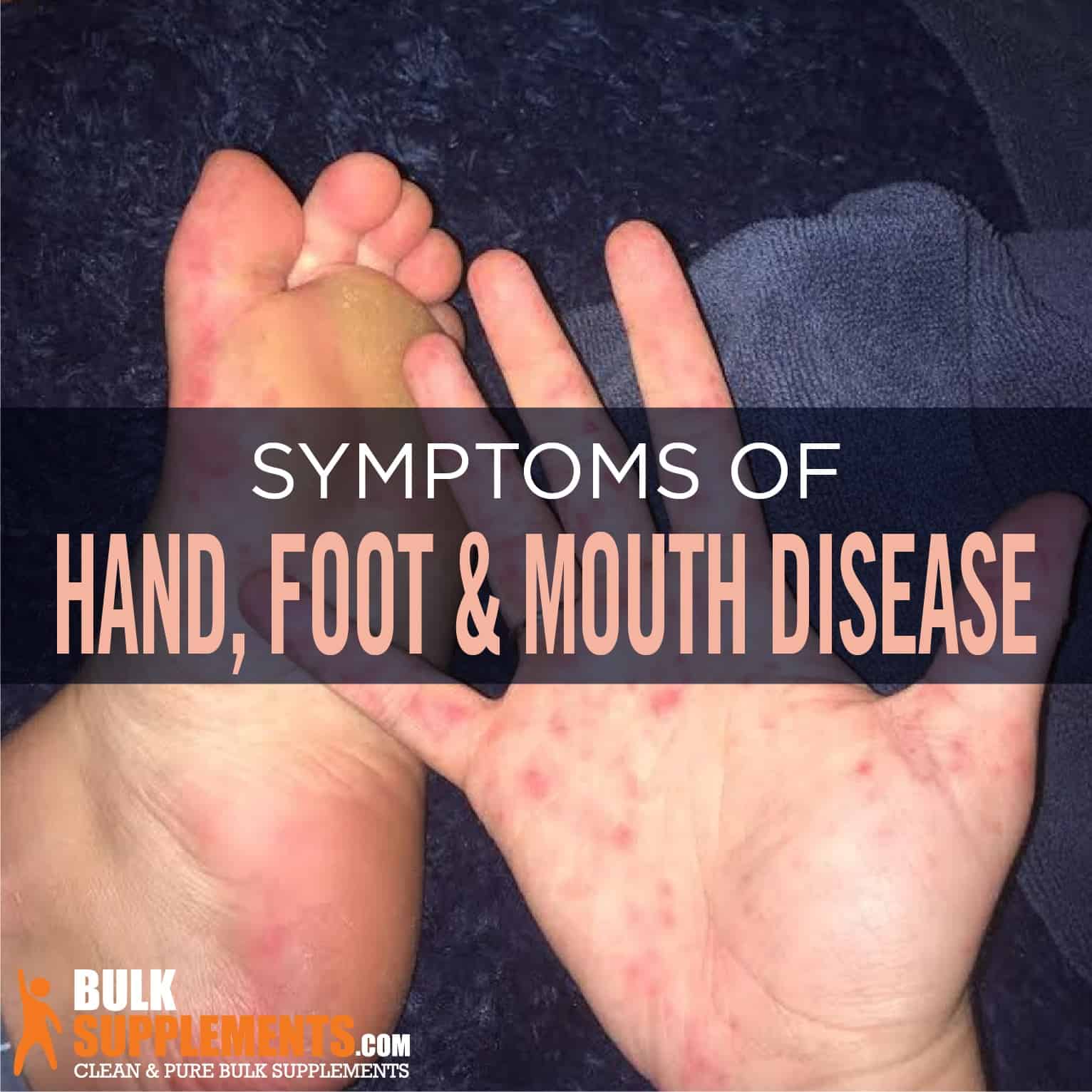
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infectious disease caused by a virus. It is characterized by a fever, mouth sores, and a rash on the hands and feet. HFMD is most commonly seen in children under the age of 5, but it can also occur in adults.
The incubation period for HFMD is typically 3-6 days. Symptoms usually appear suddenly and can include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Mouth sores
- Rash on the hands and feet
The rash associated with HFMD is typically red and bumpy. It may appear on the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, and the buttocks. The rash can be itchy and uncomfortable.
HFMD is usually a mild illness that resolves on its own within 7-10 days. However, in some cases, HFMD can lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis.
Transmission and Prevention
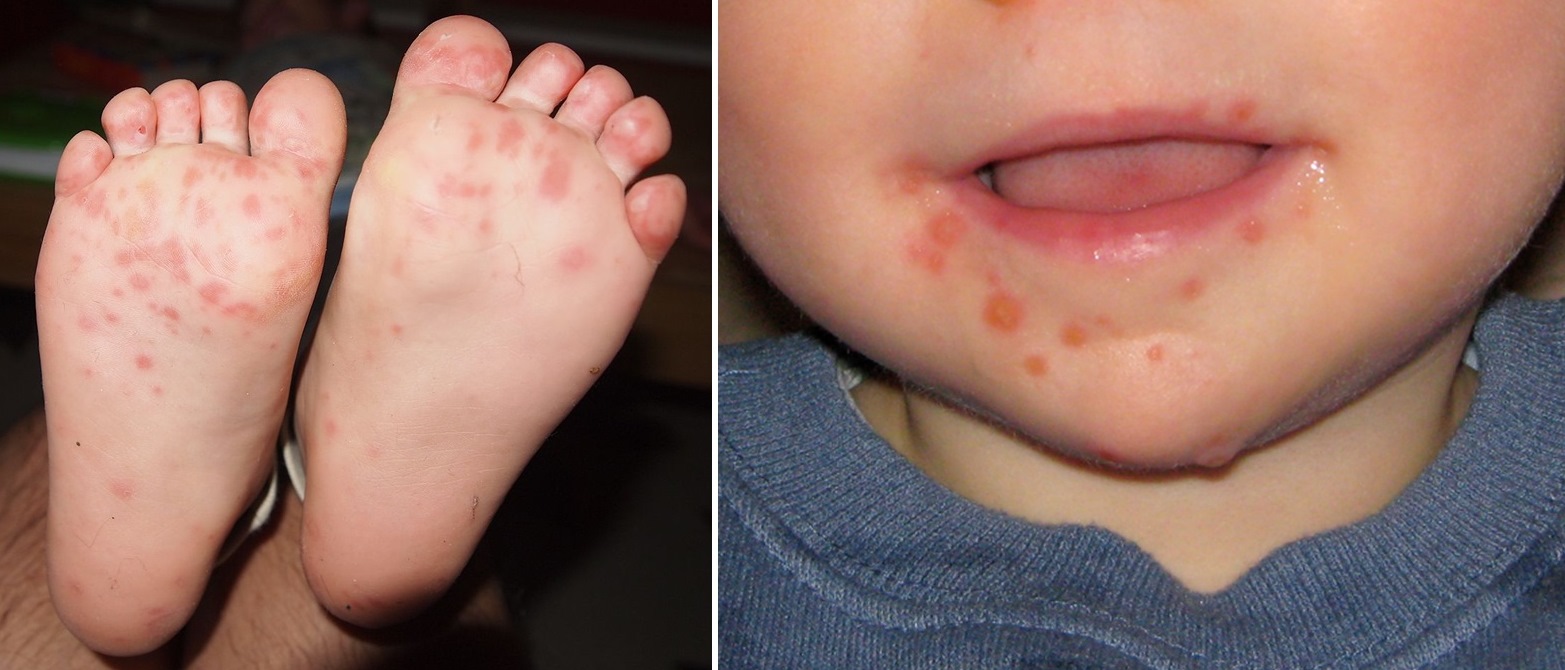
Hand foot and mouth disease – HFMD is a highly contagious disease that can be spread through contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces. The virus is present in the saliva, mucus, and feces of infected individuals, and it can be transmitted through coughing, sneezing, or touching contaminated objects.
There are several preventive measures that can be taken to avoid contracting HFMD. These include:
Frequent handwashing
Washing your hands frequently with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of HFMD. It is especially important to wash your hands after coming into contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces.
Disinfection
Disinfecting surfaces that may be contaminated with the virus can help to prevent its spread. This includes surfaces such as doorknobs, countertops, and toys.
Avoiding contact with sick individuals
If you are exposed to someone who is infected with HFMD, it is important to avoid close contact with them. This means avoiding touching them, sharing food or drinks, or using their personal belongings.
Vaccination
There is a vaccine available to prevent HFMD. The vaccine is recommended for children between the ages of 6 months and 5 years. It is given in two doses, and it is effective in preventing the majority of cases of HFMD.
Treatment and Management: Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is typically a mild and self-limiting viral infection. However, some cases may require medical attention. Treatment focuses on supportive care and symptom management.
There is no specific antiviral medication for HFMD. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
Supportive Care
- Rest: Encourage the patient to rest and avoid strenuous activities.
- Hydration: Dehydration is a common complication of HFMD, especially in young children. Offer plenty of fluids, such as water, electrolyte solutions, or clear broths.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce fever and pain.
Antiviral Medications, Hand foot and mouth disease
In severe cases, antiviral medications may be prescribed to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. These medications are most effective when started early in the course of the illness.
Managing Symptoms at Home
Most cases of HFMD can be managed at home with supportive care. Here are some tips:
- Rest: Encourage the patient to rest and avoid strenuous activities.
- Hydration: Offer plenty of fluids, such as water, electrolyte solutions, or clear broths.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce fever and pain.
- Mouth sores: Rinsing the mouth with salt water or a mouthwash can help relieve pain and discomfort from mouth sores.
- Skin lesions: Keep the skin lesions clean and dry. Avoid scratching or picking at the lesions.
Potential Complications
Most cases of HFMD are mild, but complications can occur, especially in young children and those with weakened immune systems. These complications may include:
- Dehydration: Dehydration can occur if the patient is not able to drink enough fluids. Dehydration can lead to serious complications, such as seizures or kidney failure.
- Meningitis: Meningitis is a rare but serious complication of HFMD. Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes that line the brain and spinal cord.
- Encephalitis: Encephalitis is a rare but serious complication of HFMD. Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if the patient has any of the following symptoms:
- High fever (over 101 degrees Fahrenheit)
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Drowsiness or confusion
- Difficulty breathing
- Vomiting or diarrhea that cannot be controlled
- Skin lesions that are spreading or becoming infected
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common childhood illness, is caused by a virus. The virus can spread through contact with respiratory droplets or contaminated surfaces. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth.
While the Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit, Michigan, they have no relation to hand, foot, and mouth disease. The virus that causes hand, foot, and mouth disease is not spread through contact with animals.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common childhood illness, can cause fever, sores, and a rash. While not usually serious, it can be uncomfortable. For more information on this and other childhood illnesses, read the biden interview. The interview discusses the importance of early childhood education and healthcare, which can help prevent and treat childhood illnesses like hand, foot, and mouth disease.